Process requirements for laser cutting stainless steel thick plates
With the continuous development of laser cutting technology, the utilization rate of 10,000-watt models in the market continues to increase, and the application fields of stainless steel medium and thick plates are also becoming increasingly wider. At present, products made of stainless steel thick plates have been widely used in shipbuilding, bridge engineering, machinery manufacturing, construction engineering and other industries.
According to current process standards, the best way to cut stainless steel thick plates is to use a high-power laser cutting machine. As an expert in 10,000-watt laser cutting applications, Rayma Laser's technical R&D team is committed to continuously developing new technologies to improve the cutting effect of its products. After the team continuously summarized their experience, they summarized the stainless steel thick plate cutting process skills for reference by colleagues and end customers——
Process requirements for laser cutting stainless steel thick plates
Generally speaking, medium plates refer to steel plates with a thickness of 10.0-25.0mm, those with a thickness of 25.0-60.0mm are called thick plates, and those with a thickness exceeding 60.0mm are called extra-thick plates. In actual cutting, the quality of thick plate cutting is mainly evaluated comprehensively from several aspects such as roughness, verticality, cutting width, texture, burrs, heat-affected area size, and whether the plate is deformed during cutting.
Specifically, if you want to cut high-quality stainless steel thick plate workpieces, you need to pay attention to the following points in the process -
01 Nozzle selection
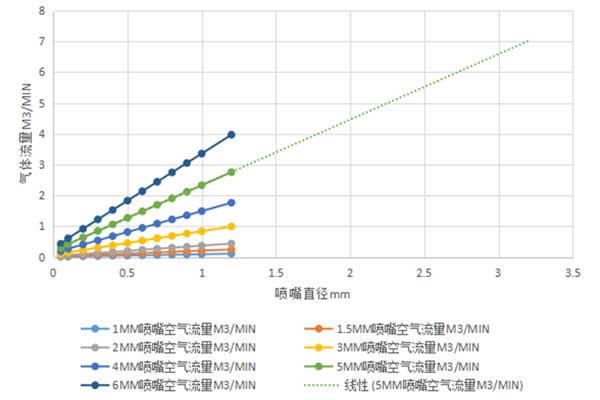
The diameter of the nozzle determines the shape of the airflow entering the incision, the gas diffusion area, and the gas flow rate, thereby affecting the stability of melt removal and cutting. The greater the air flow entering the incision, the faster the speed, and the proper position of the workpiece in the air flow, the stronger the ability of the jet to remove molten material. The thicker the stainless steel, the larger the nozzle should be used, and the larger the proportional valve should be set. Only by increasing the flow rate can the pressure be ensured and the normal cross-section effect be achieved.
Specifications: The specifications of the nozzle here mainly refer to the end hole diameter. Taking Precitec's cutting nozzle as an example, its hole diameter ranges from 1.5mm to 5.0mm. The choice of aperture is mainly related to the cutting power. The greater the power, the more heat is generated and the greater the air volume is required. When we cut plates below 3mm, we generally use nozzles with apertures of 2.0mm; when cutting plates from 3mm to 10mm, we use 3.0mm nozzles; when cutting plates above 10mm, we use nozzles of 3.5 and above.
Single-layer nozzle: Generally speaking, double-layer nozzles are used for oxidative cutting (auxiliary gas is oxygen), and single-layer nozzles are used for melting cutting (auxiliary gas is nitrogen). However, some lasers have special instructions on whether to use single layer or double layer. In this case, just follow the laser instructions.
02 Auxiliary gas selection and gas purity
Nitrogen and nozzle diameter & gas pressure test data chart
Various auxiliary gases are often used in stainless steel laser cutting, such as oxygen, nitrogen, air, etc. Different gas types are used to produce different cutting section effects. Oxygen has a black cross-section, which has a high cutting speed and can cut thick plate materials. The purity is recommended to be ≥99.999%; air is light yellow; nitrogen can keep the original color of stainless steel from being oxidized, so the workpiece does not need to be reprocessed. The purity is recommended to be ≥99.995%. . Nitrogen is the preferred auxiliary gas for stainless steel cutting.
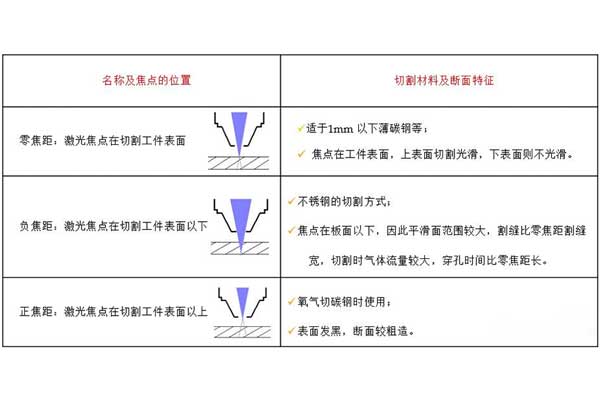
03 focus position
The focus is different, and the thickness, material, and quality that can be cut are also different. When cutting different materials and thicknesses, different focus needs to be adjusted. Before cutting, the actual zero focus is measured, and the cutting process parameters can be tested and analyzed based on the zero focus. Negative defocus is the main process selection direction for stainless steel cutting.
04 The impact of laser frequency adjustment on cutting
Effect of frequency changes on stainless steel thick plate cutting:
The frequency decreases from the range of 500-100Hz, the cutting section effect becomes finer, and the layering gradually improves. When the frequency is set to 100Hz, it cannot cut and reflects blue light. Find the optimal frequency range by changing the frequency. In order to ensure the best cutting section, the number of pulses must be perfectly matched with the energy of the single pulse.
Effects of changes in pulse duty cycle on stainless steel thick plate cutting:
The pulse duty cycle of 45% is the critical value. If the duty cycle continues to decrease, uncut traces will appear on the lower surface. When the duty cycle increases to 60%, the cross section will become rough, the layering will be obvious, and the cutting surface will turn yellow.
Ritman Laser: Expert in 10,000-watt laser cutting applications
At a time when laser technology is developing rapidly, Ruima Laser is forging ahead with determination, taking "precision quality, ingenious products" as its original intention, using technology research and development as the driving force to promote the market, paying close attention to the long-term development of the brand, and in product update iterations and process knowledge sharing. , New technological innovation has always been at the forefront of the industry. When choosing a laser cutting machine, choose Rayma Laser!